 |
 |
- Search
| J Environ Anal Health Toxicol > Volume 26(3); 2023 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
This study focuses on quantifying the impact of various factors on nonylphenol analysis and identifying the key contributors affecting the analytical outcomes. We calculated the measurement uncertainty arising from the analysis process using GC-MS, aiming to pinpoint uncertainty sources, quantify them numerically and then calculated the overall uncertainty through uncertainty synthesis. The results revealed that factors such as calibration curve construction, internal standard injection, and reproducibility through repeated testing significantly influenced the synthetic standard uncertainty. Negligible effects were observed during processes, involving concentration and filling the standard volume post-purification, as well as during sample collection. The relative expanded uncertainty for nonylphenol concentration was within 4.6%. The uncertainty contributions from each step were as follows: sample collection, calibration curve construction, injection of internal standards, filling of the 1 mL standard volume, and reproducibility from repeated testing accounted for 0.0%, 92.7%, 4.0%, 0.1%, and 3.2% of the total uncertainty, respectively.
지난 30여년 동안 인간과 생태계에 대한 EDCs(Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals)의 심각한 영향으로 인해 다양한 화학물질에 대하여, 다양한 분석방법으로 EDCs 판정을 위한 평가가 이루어져 왔다. UNEP(United Nations Environment Programme)에서는 최근 EDCs 및 잠재적 EDCs에 대한 목록 및 관련 평가결과들을 발표하였으며 그 중 대표적인 EDCs가 알킬페놀(alkylated phenols), 비스페놀(bisphenols) 그리고 프탈레이트 에스테르(phthalate esters) 인 것으로 알려져 있다[1-3].
일본에서는 비스페놀 A, OPs(Octylphenols), NPs(Nonylphenols) 등이 어류에 대한 내분비계 교란물질로 알려져 있으며 이들 중 OPs와 NPs는 비이온성 세제 즉 알킬페놀 에톡실레이트(Alkylphenol Ethoxylates, APEOs)의 분해산물로서 그들의 광범위한 사용과 폐기 후 폐수처리시설 등 대부분의 물환경에서 발생되기 시작하여 생활환경에서 빈번하게 검출되어왔다[4-8].
Ruhí [9-10]등에 의하면 지하 대수층의 상당 부분이 ng/L 또는 μg/L 범위의 저농도이지만 EDCs로 오염되어 있는 것으로 보고되고 있으며, 일반적으로 그들은 세제, 향수, 크림 등의 제품에 함유된 첨가물로 사용된 후 물환경에서 발견되는데 내분비계 교란 또는 장기의 비정상적 발달과 같은 인간에 해로운 영향을 끼칠 수 있는 것으로 알려져 있다[11-13].
이들 EDCs 중 주목할 만한 것이 NPs인데, NPs의 구성성분인 짧은 사슬의 APEOs는 계면활성 특성이 있어 세제, 농약, 플라스틱 포장재, 화장품 제제 등에 광범위하게 사용되며 이들이 환경생태계에 버려졌을 때 미생물학적 작용으로 인해 NPs로 전환된다[14]. 이러한 취급, 사용, 변환 등의 과정을 거쳐 하수 슬러지 중에서 NPs가 고농도로 검출되고 있어 하·폐수 처리 및 보건, 환경 위생상 중요한 이슈로 대두되고 있다[15].
이와 관련 국내에서는 NPs이 2022년 이후 수질감시항목으로 관리, 운영되고 있는데 NPs 분석 시 추출용매 안에 함유된 불순물 그리고 분석대상 시료의 매트릭스로부터 방해물질이 추출되어 분석 결과값에 영향을 미칠 수 있으며 13개 이성질체 분석 결과값을 합산하는 과정을 포함하여 용매추출, 정제, 농축 등 복잡한 전처리 과정을 수행함에 있어 불확도 요인이 다양하게 존재하며 결과값의 표준편차 또한 높을 것으로 우려된다[16-17]. 또한 이러한 결과값은 환경부의 수질오염물질 지정 등에 관한 지침에 따라 감시항목 운영 및 관리절차를 거친 후 수질오염물질 또는 특정수질 유해물질로 지정되는 등 국가 수질오염물질 관리에 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있다[18].
측정결과는 반복측정으로 인해 얻어진 일련의 관측을 근거로 산출되는데 이때 반복측정에서의 변동은 측정결과에 영향을 미치는 요인들이 일정하게 유지되지 않기 때문에 발생한다. 특히 실제 분석과정에서는 분석결과로 산출하는 수학적 모델이 일반적으로 분석값 이외의 정확히 알려 지지 않은 여러 요인을 포함하기 때문에 이러한 요인을 정확히 알고 산출 결과에 반영하는 것은 매우 중요하다[19].
또한 일반적인 화학 분석실의 분석 과정에서 화학분석 절차의 유효성과 관련된 품질요소는 측정량 또는 결과값의 품질을 보증하기 위한 가장 중요한 조건들로써 QA/QC 및 불확도 계산에서도 가장 중요하게 취급하여야 할 요소들이다[20-21].
이러한 감시항목 및 국가 수질오염물질에 대한 관리, 결과값의 품질보증 등 주요 사항들을 고려하여 본 연구에서는 산업폐수 중 NPs 분석 시 영향을 줄 수 있는 요인별 영향을 수치화하고 분석 결과값에 영향을 미치는 주요 영향인자를 찾아보고자 하였으며 요인별 측정 불확도를 산출하여 분석결과의 통계적 신뢰도 수준으로 활용하고자 하였다.
본 연구에 사용된 용매(methanol, dichloromethane)는 Wako(Japan)사의 잔류농약분석용 시약을 사용하였고 증류수는 Milli-Q water purification system을 통과한 3차 증류수를 이용하였다. NPs의 표준품(2,500 mg/L ± 2.4%, k = 2)과 내부표준품으로 사용한 phenanthrene- d10(1,015 mg/L ± 2.4%, k = 2.95)은 AccuStandard사로부터 구입하였다. 용매추출 후 수분제거를 위해 사용된 무수황산나트륨(sodium sulfate anhydrous)은 Wako사의 잔류농약분석용 시약을 사용하였고, 시료정제용 Florisil cartridge는 Waters사의 sep-pak®(500 mg/3 mL) cartridge를 이용하여 dichloromethane으로 활성화시킨 후 사용하였다.
분석용 시료는 사전분석을 통해 검출빈도가 높았던 전기, 전자업종의 폐수시료 중 전체 검출농도(0.00~0.04 mg/L)의 중간범위이면서 수질오염공정시험기준[17] 정량한계(0.002 mg/L) 이상인 폐수를 선정하여 이 시료 0.5 L를 1 L 분액깔때기에 취하여 내부표준물질 phenanthrene-d10 (AccuStandard, 1,015 mg/L ± 2.4%)을 methanol에 10 mg/L로 희석한 것을 100 μL 첨가하고, NaCl(Wako, 잔류농약분석용) 30 g을 넣어 녹인 후, dichloromethane(Wako, 잔류농약분석용) 50 mL로 2회 반복 추출 후 dichloromethane 층을 1PS 여지(Whatman, d110 mm)를 이용하여 무수황산나트륨(Wako, 잔류농약분석용)으로 수분을 제거하고 질소농축기로 0.7 mL까지 농축하였다.
Dichloromethane 1 mL로 2회 활성화시킨 Florisil cartridge(Waters, sep-pak® 500 mg/3 mL, 50-200 μm)를 통과시켜 정제된 시료는 다시 농축관에 옮겨 0.5~0.7 mL까지 농축한 후 dichloromethane을 첨가하여 최종 부피 1 mL로 하였다. 시료의 전처리 과정을 Fig. 1에 요약하여 나타내었다.
검정 범위는 NPs 표준물질을 혼합한 5개의 검정용 표준 혼합물(2, 4, 10, 20, 40 μg/L)을 만들어 폐수 분석용 시료와 동일한 전처리 과정을 거쳐 GC-MS(PerkinElmer, Clarus 600)로 분석하였으며 세부 분석조건은 Table 1과 같다.
각 표준용액 농도 별 크로마토그램으로부터 피크의 머무름 시간을 확인하고, 내부표준물질의 피크면적에 대한 분석대상물질(NP1~NP13)의 농도 별 면적합의 비로 검정 곡선을 작성하였다. 즉 NPs 표준물질 내 구성비율이 다른 13개의 이성질체가 존재하는 NPs 표준용액 5개의 각 농도 별 정량 면적의 합을 계산해 검량선을 작성하여 시료 정량에 적용하였으며 대상물질 별 선택이온은 Table 2에 나타내었다.
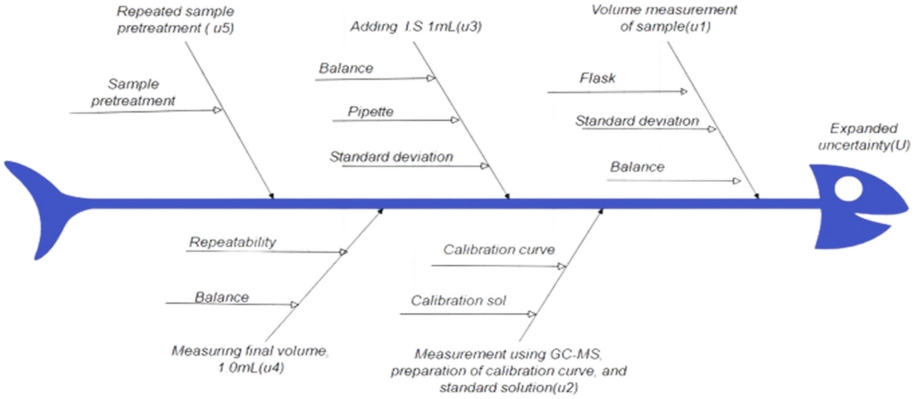
산업폐수 중 NPs의 분석은 수질오염공정시험기준[17]에 따라 실시하였으며 분석과정은 시료 분취, 추출, 농축, 정제 등 시료 전처리 과정과 표준품의 희석 그리고 GC-MS를 이용한 기기분석 과정으로 구분된다(Fig. 1). 산업폐수 중 NPs의 분석 관련 불확도 인자는 크게 시료 분취, 표준물질의 순도 및 표준용액 제조, 검정 곡선의 작성, 농축·정제 후 특정 부피(1 mL)를 채우는 과정, 내부표준용액 1 mL를 주입하는 과정, 반복시험에 의한 전처리 과정의 불확도 등의 요소를 산정하였다. NPs 분석과정의 불확도 요인 및 산출과정을 Fig. 2에 도식화 하였다. 분석용 표준물질로 NPs의 경우 AccuStandard 2,500 mg/L ± 2.4%, k = 2, 내부표준물질로 Phenanthrene-d10 1,015 mg/L ± 2.4%, k = 2.95(k; 포함인자(coverage factor), 확장불확도를 구하기 위해 합성표준불확도에 곱하는 수치 인자)를 사용하였으며 표준물질 및 분석용 플라스크, 피펫의 경우 직사각형분포(rectangular distribution)를 적용하였고 분석용 저울의 경우 교정성적서에 표기된 불확도를 적용하여 표준불확도를 산출하였다. 이와 같이 GUM(Guide to the Expression of the Uncertainty of Measurement) [22] 및 측정결과의 불확도 추정 및 표현을 위한 지침(KOLAS) [23]에 따라 Fig. 2에서와 같이 분석 전과정에서 시험에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 주요 요인들을 찾아내고 그 주요 요인별 세부영향요인에 대한 표준불확도(u)를 먼저 수치화하고, 수치화된 표준불확도를 각 요인별 농도단위에 따라 상대표준불확도(ur)를 산출한 후 불확도전파법칙에 따라 각 요인별 상대표준불확도를 합성하여 주요 요인별 상대합성표준불확도(ur)를 구하고 다시 산정된 주요 요인별 상대합성 표준불확도로부터 측정모델에 불확도 전파법칙을 적용하여 합성표준불확도(Ur)를 구하였으며 여기에 신뢰수준 95%에 상당하는 포함인자(k)를 곱하여 확장불확도(U)를 산출하였다.
또한 전체 상대합성 표준불확도에 각 불확도 요인들이 미치는 영향의 정도를 기여율로 표시하여 불확도 주요 요인을 파악보고자 하였다. 기여율의 산정방식은 다음과 같다.
기여도(%) = ui2(xi) / uc2(Cx)
(ui2(xi); 각 요인별 상대표준불확도, uc(Cx); 각 요인별 불확도를 합성한 전체 상대합성표준불확도)
분석용 시료 부피(0.5 L) 분취 시 불확도(ursd) 산출을 위하여 시료를 0.5 L 10회 분취 후 무게를 측정하여 표준편차로부터 표준불확도(usd) 및 상대합성 표준불확도(ursd)를 산출하였으며
usd = (10회 무게측정 표준편차)/n1/2 = 0.492 7/101/2 = 0.155 8 g,
ursd = usd/(10회 평균무게) ×100 = 0.155 8/501.849 × 100 = 0.031 0%
사용된 부피플라스크(0.5 L)의 표준불확도(ufla)는 제조사에서 제공하는 최대 허용오차(500 ± 0.06 ml) 자료를 이용하였다.
ufla = 최대허용차/31/2 = 0.06/31/2 = 0.034 6 mL
urfla = ufl/500 × 100 = 0.006 9%
무게 측정을 위한 저울의 불확도(urbal)는 교정성적서의 불확도를 이용하였다.
ubal = 교정성적서 불확도/포함인자(k) = 0.000 2/1.96 = 0.000 1 g
urbal = ubal/500 × 100 = 0.000 0%
분석용 시료 부피 측정과정에서 발생하는 불확도는 500 mL 10회 무게측정, 용량 플라스크, 저울에 대한 세 가지 불확도 인자로부터 불확도 전파법칙에 따라 합성하여 상대합성 표준불확도(urvol)를 산출하였으며 그 결과는 다음과 같다.
urvol = (ursd2 + urfla2 + urbal2)1/2 = 0.031 8%
분석용 시료 부피 측정과정에서의 자유도(νeff)는 Welch-satterthwaite 공식을 이용하여 합성하였으며 자유도가 무한대의 경우 수치 1,000,000을 적용하였다.
νeff = uc4(y) / Σ([ciu(xi)]4 / νi) = u4/(ursd 4/n-1 + urfla 4/∞ +0.000 04/∞)
(uc4(y); 합성표준불확도, ciu(xi); 요인별 상대표준불확도, νi; 요인별 자유도)
= 0.031 84/(0.031 04/9 + 0.006 94/1,000,000 + 0.000 04/1,000,000) = 9.9
검량선 작성 시 불확도(urcal) 산출을 위하여 5점 검량선 회귀분석을 실시하여 회귀분석 시 불확도(ureg)를 산출하였고 검량선 작업 전 표준용액 제조과정의 불확도 산출을 위하여 표준물질 순도 및 표준용액, 단계별 표준용액 제조시 사용된 플라스크, 피펫의 표준불확도를 각각 산출 후 합성(urstd)하였고 다시 회귀분석 시 불확도(ureg) 및 표준용액 제조과정의 불확도(urstd)를 합성하여 검량선 작성 시 상대합성 표준불확도(urcal)를 산출하였다.
ureg = s/b1 × ((1/p + 1/n + (c0-c)/sxx)1/2
회귀분석 후 결과 수치를 입력을 하면
ureg = 0.206/183.732 × (1/5 + 1/5 + (0.020-0.015) / 0.000 3)1/2 = 0.000 8 mg/L
urreg = (ureg/측정값평균) × 100 = (0.000 8/0.020) × 100 = 3.856 3 %
회귀분석 과정에서의 자유도(vrreg)는 다음식과 같이 산출하였다.
vrreg = (ucal4) / ((s/b1 × (1/p)1/2)4/(p-1) + (s/b1 × (1/n + (c0-c)2/sxx))1/2) / (n-2))
= (0.000 84) / ((0.000 54 / 2) + (0.000 64/ 3)) = 5.0
(b1: 기울기, p: 1개 시료당 분석 횟수, n: 전체 측정 횟수, c0: 시료농도의 측정값, c: 표준용액 평균농도 s: 잔차의 표준편차 sxx: 표준편차 제곱의 합(표준물질 입력량들의 변동값))
표준용액 제조과정 불확도(urstd)의 경우 NPs 표준물질, 희석에 사용된 플라스크와 피펫의 불확도 각각을 산출한 후 두점교정법을 적용하여 불확도를 합성하였으며 그 과정은 아래와 같다.
NPs 표준물질 2,500 mg/L, 인증값 2.4%(95%, k = 2)으로부터
표준물질 불확도(ust) = 2,500 × 2.4 × 0.01/k = 30.0 mg/L,
상대합성 표준불확도 urst = ust / 2,500 × 100 = 1.2%
표준원액 및 각 단계별 표준용액 희석과정의 불확도는 다음식과 같이 산출하였으며 그 결과는 Table 3과 같다.
u(Cstock) = Cstock × ((u(cstd)/cstd)2 + (u(vpipet)/vpipet)2 + (u(vvol)/vvol)2)1/2
(Cstd : 표준용액 조제농도, Cstock : 표준원액 농도, vpipet: 피펫 부피, vvol: 플라스크 부피)
두점교정법을 적용하여 표준용액 각각의 불확도를 아래 식과 같이 합성하여 표준용액 제조과정의 상대합성 불확도(urcal)를 산출하였으며 각 표준물질 단계별 자유도는 무한대(∞)로서 자유도 값은 1,000,000을 적용하였다.
urstd = ((ustock2 × νstock + ust12×νst1 + ust22×νst2 + ust32 × νst3 +ust42 × νst4 + ust52 × νst5) / (νstock + νst1 + νst2 + νst3 + νst4 + νst5))1/2 = 2.087 1%
5점 검량선 회귀분석 및 표준용액 제조과정의 불확도를 합성한 결과(urcal)는 다음과 같다.
urcal = (urreg2+urstd2)1/2 = 4.384 9%
검량선 작성 시 유효자유도는 Welch- satterthwaite 공식을 이용하여 합성하였으며 그 결과는 아래와 같다.
νeff = uc4(y) / Σ([ciu(xi)]4 / νi) = 4.384 94 / ((3.856 34 /5.0) + (2.087 14 / 1,000,000)) = 8.3
내부표준용액 첨가(1 mL) 시 발생하는 불확도(uris)의 경우 피펫으로 1 mL 취한 후 10회 무게를 측정하여 표준편차로부터 불확도(ursd)를 산출하였으며 사용된 피펫의 불확도(urpip), 무게 측정을 위한 저울의 불확도(urbal)를 주요 인자로 산출하였다.
저울불확도(ubal) = 교정성적서 불확도/k = 0.000 2/1.96 = 0.000 1 g
urbal = ubal/1×100 = 0.008 2%
피펫불확도(upipet) = 최대허용오차 / (3)1/2 = 0.06/(3)1/2 = 0.034 6 mL
urpipet = upipet/1 × 100 = 0.060 0%
피펫으로 1 mL 취한 후 10회 무게 측정 후 표준편차로부터
표준편차 불확도(usd) = 표준편차/n1/2 = 0.022 8/10 1/2 = 0.007 2 g
상대합성 표준불확도(ursd) = usd/10회 평균 × 100 = 0.007 2 / 0.792 × 100 = 0.910 2%
위 세가지 불확도를 합성하여 내부표준용액 첨가(1 mL) 시 불확도(uris)를 다음과 같이 합성하였다.
uris = (ursd2 + urpip2 + urbal2) = 0.910 22 + 0.006 02 + 0.008 22 = 0.912 2%
내부표준용액 첨가(1 mL)시 자유도(νis)는 아래와 같이 Welch-satterthwaite 공식을 적용하였다.
νis = uc4(y) / Σ([ciu(xi)]4 / νi) = 0.912 24 / (0.910 24/(10-1)) + (0.060 04/ 1,000,000))+(0.008 24/1,000,000) = 9.1
농축, 정제 후 최종부피(1 mL) 맞춤 시 불확도(urmu)의 경우 dichloromethane을 첨가하여 1 mL 표선 맞춤을 10회 반복한 후 무게를 측정하여 표준편차로부터 불확도(ursd)를 산출하였으며 무게측정을 위한 저울불확도(urbal)도 불확도 요인에 포함하였다. 표선 1 mL 맞춤 후 10회 무게 측정값의 표준편차로부터
표준불확도 (usd) = 표준편차/n1/2 = 0.005 9/101/2 = 0.001 9 g
상대합성 표준불확도(ursd) = usd/10회 평균 × 100 = 0.001 9/ 1.291 × 100 = 0.144 5%
저울불확도(ubal) = 교정성적서 불확도/k = 0.000 2/1.96 = 0.000 1 g
urbal = ubal/1 × 100 = 0.008 2%
상기 두 가지 불확도를 합성하여 최종부피(1 mL) 맞춤 시 불확도(umassup)를 다음과 같이 산출하였다.
urmassup = (ursd2 + urbal2)1/2 = (0.144 52 + 0.008 22)1/2 = 0.144 7%
최종부피(1 mL) 맞춤 시 자유도(νmassup)
νmassup = uc4(y) / Σ([ciu(xi)]4/νi) = 0.144 74/(0.144 54/(10-1) + 0.008 24/1,000,000) = 9.1
산출된 불확도 요인 외 재현성 등 고려되지 못한 미세한 요인들과 시료의 분취부터 전처리, 기기분석 등 전과정에서 발생할 수 있는 기타 불확도 요인까지 모두 포함하고자 5회에 걸쳐 실험 전과정을 수행하였으며 그 결과의 산포값으로부터 불확도를 산출하여 다음과 같이 상대 합성 표준불확도(urscat)를 구하였다.
표준불확도(uscat) = 표준편차/n1/2 = 0.000 4/51/2 = 0.000 2 mg/L
상대합성 표준불확도(urscat) = uscat /평균×100 = 0.000 2/0.020 × 100 = 0.817 6%
반복시험에 의한 전처리 과정의 자유도(vrscat) = n-1 = 4.0
산정된 각 요인별 불확도로 부터 불확도 전파법칙을 적용하여 상대합성 표준불확도(Ur)를 산출하였으며 Welch-Satterthwaite 등식에 요인별 자유도와 상대합성 표준불확도를 적용하여 유효자유도(Ve)를 구하였다.
Ur = (urvol2 + urcal2 + uris2 + urmassup2 + urscat2)1/2 = (0.031 82 + 4.384 92 + 0.912 22 + 0.144 72 + 0.817 62)1/2 = 4.555 2%
Ve = (Ur4)/((urvol4/vrvol)(urcal4/vrcal) + (uris4/vris) + (urmassup4/vrmassup) + (urscat4/vrscat)) = (4.55524)/((0.031 84/9.9) + (4.384 94/8.3) + (0.912 24/9.1) + (0.144 74/9.1) + (0.817 64/4.0)) = 9.6
포함인자(k)를 구하기 위해 신뢰수준 95%, 유효자유도 9.6으로부터 TINV 함수를 적용하여 t 값을 구하고
t 값(신뢰수준 95%) = TINV(0.05, 9.6) = 2.262
k 값과 상대합성 표준불확도의 곱으로부터 확장불확도(U)를 산출하였다.
U = k × Ur = 2.262 × 4.555 2 = 10.30%,
NPs 측정값에 대한 불확도는 0.020 mg/L × 10.30 × 0.01 = 0.002 mg/L
따라서 폐수 중 NPs 농도측정값 0.020 mg/L에 대한 확장불확도는 Table 4와 같이 표현되며 산업폐수 중 NPs 분석과정의 불확도 산출결과를 Table 5에 정리하였다.
Table 5에서와 같이 산업폐수 중 NPs 분석 시 영향을 줄 수 있는 요인별 영향을 수치화하고 분석 결과값에 영향을 미치는 주요 영향인자를 조사한 결과 검량선 작성을 위한 회귀분석에서 상대표준불확도 3.856 3%, 기여도 71.67%, 표준용액 조제과정에서 상대표준불확도 2.087 1%, 기여도 20.99%, 내부표준용액 주입과정에서 상대표준불확도 0.910 2%, 기여도 3.99%, 반복시험에 의한 재현성 조사에서 상대표준불확도 0.817 6%, 기여도 3.22% 순으로 높게 나타 났으며 나머지 불확도 요인들은 상대표준불확도 0.144 7%, 기여도 0.1% 이하로서 전체 불확도 수준에 미치는 영향은 미미한 것으로 조사되었다. 검량선 작성을 위한 회귀분석과정과 표준용액 희석과정이 가장 높은 불확도 요인으로 나타났으며 내부표준용액 주입과정 3.99%, 전처리 과정 반복시험 3.22% 순으로 높게 나타났다. 주요 불확도 요인별 기여도 조사결과는 시료 분취, 검량선 작성, 내부표준용액 주입, 부피 1 mL 표선 채움, 반복시험에 의한 재현성 각각의 불확도 비율은 0.00%, 92.66%, 4.01%, 0.1%, 3.22% 로 분석결과에 큰 영향을 미치는 요인은 검량선의 작성 특히 회귀분석 시 검량선의 비직선성 및 표준용액의 제조과정, 내부표준용액 주입, 반복시험에 의한 재현성 불확도 3가지 요인이 주요 불확도 요인으로 평가되었다.
본 연구에서는 GC-MS를 이용하여 산업폐수 중 NPs의 농도를 측정하는 과정 중 발생되는 측정불확도를 산출하였다. 검토된 불확도 요인은 크게 시료 분취, 검량선의 작성, 내부표준용액 주입, 농축, 정제 후 부피 1 mL 표선을 채우는 과정, 반복시험에 의한 재현성 불확도 5가지로서 각각의 불확도 비율은 0.00%, 92.66%, 4.01%, 0.1%, 3.22% 이었다. NPs 측정농도의 상대확장불확도는 10.30% 이내였다. 불확도에 큰 영향을 미치는 요인은 검량선의 작성, 내부표준용액 주입, 반복시험에 의한 재현성 불확도 3가지 요인이 주요 불확도 영향인자임을 확인하였다.
측정 모델의 불확도 산출 과정 중 검량선 작성 특히 회귀분석 과정에서의 불확도 정도는 대상시료의 높고 낮음에 따라 달라질 수 있는데 본 연구에서는 검출빈도가 높았던 전기, 전자업종의 비교적 낮은 농도 레벨(0.020 mg/L)을 대상시료로 하였으므로 다른 불확도 요인보다 매우 높은 영향인자로 평가되었음 또한 고려되어야 할 사항으로 판단되며 이러한 불확도 요인을 감소시키기 위하여 시료농도 범위의 표준용액 농도단계를 늘리고 피펫 사용 및 부피 채움 과정의 오차를 줄이기 위해 저울을 활용한 표준용액 조제방법 또한 하나의 대안이 될 수 있을 것으로 판단된다.
Table 1.
Analytic condition of GC-MS for nonylphenols
Table 2.
Selected Ions by nonylphenol isomers
Table 3.
The process of calculating the uncertainty of the standard solution for preparing a calibration curve
Table 4.
Expanded uncertainty (U) for determinations of nonylphenol in wastewater
Table 5.
Uncertainty factors, standard uncertainties and expanded uncertainty for determinations
참고문헌
1. United Nations Environment Programme, "Worldwide Initiatives to Identify Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) and Potential EDCs", Overview Report I, 2017
2. United Nations Environment Programme, "An Overview of Current Scientific Knowledge on the Life Cycles, Environmental Exposures, and Environmental Effects of Selected Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) and Potential EDCs", Overview Report II, 2017
3. United Nations Environment Programme, "Existing National, Regional, and Global Regulatory Frameworks Addressing Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs)", Overview Report III, 2017
4. Ministry of the Environment, "Future Actions to Endocrine Disrupting Effects of Chemical Substances", 2010, Japan
5. Z. Mao, X.-F. Zheng, Y.-Q. Zhang, X.-X. Tao, Y. Li, and W. Wang, “Occurrence and biodegradation of nonylphenol in the environment”, International journal of molecular sciences, 2012, 13, 491-505.


6. Z. Lu, and J. Gan, “Analysis, toxicity, occurrence and biodegradation of nonylphenol isomers: a review”, Environment International, 2014, 73, 334-345.


7. A. Careghini, A. F. Mastorgio, S. Saponaro, and E. Sezenna, “Bisphenol A, nonylphenols, benzophenones, and benzotriazoles in soils, groundwater, surface water, sediments, and food: a review”, Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22, 5711-5741.




8. I.-H. Acir, and K. Guenther, “Endocrine disrupting metabolites of aklylphenol ethoxylates-A critical review of analytical methods, environmental occurrences, toxicity, and regulation”, Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 635, 1530-1546.


9. A. Ruhí, V. Acuña, D. Barceló, B. Huerta, J. R. Mor, S. Rodríguez-Mozaz, and S. Sabater, “Bioaccumulation and trophic magnification of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in a Mediterranean river”, Science of The Total Environment, 2016, 540, 250-259.


10. E. Koumaki, D. Mamais, and C. Noutsopoulos, “Assessment of the environmental fate of endocrine disrupting chemicals in rivers”, Science of The Total Environment, 2018, 628-629, 947-958.


11. C. G. Campbell, S. E. Borglin, F. B. Green, A. Grayson, E. Wozei, and W. T. Stringfellow, “Biologically directed environmental monitoring, fate, and transport of estrogenic endocrine disrupting compounds in water”, Chemosphere, 2006, 65, 1265-1280.


12. P. Valbonesi, M. Profita, I. Vasumini, and E. Fabbri, “Contaminants of emerging concern in drinking water: Quality assessment by combining chemical and biological analysis”, Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 758, 143624.


13. H. Park, and K. Kim, “Urinary levels of 4-nonylphenol and 4-t-octylphenol in a representative sample of the Korean adult population”, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19, 7214.



14. K. H. Langford, and J. N. Lester, "Fate and behavior of endocrine disrupters in wastewater treatment processes. In Endocrine Disrupters in Wastewater and Sludge Treatment Processes", 2002, 64-68, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA
15. I. Aparicio, J. L. Santos, and E. Alonso, “Limitation of the concentration of organic pollutants in sewage sludge for agricultural purposes”, Waste Management, 2009, >29, 1747-1753.
16. 환경부. "수질오염물질 감시항목 검사계획", 2021
17. 환경부. "수질오염공정시험기준", 2022
18. 환경부, "수질오염물질 지정 등에 관한 지침", 2022, 환경부훈령 제1558호
19. BIPM, IEC, IFCC, ILAC, ISO, IUPAC, IUPAP and OMIL, "Evaluation of measurement data-Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement", 2008, Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology
20. T. J. Farrant, "Practical Statistics for the analytical Scientist: a bench guide", 1997, Royal Society of Chemistry, UK
21. P. Gans, "Data fitting in the Chemical Sciences by the Method of Least Squares", 1992, Wiley, UK
22. ISO, "Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurements", 2022
23. 한국표준과학연구원, "측정불확도 표현 지침", 2021
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- 1,114 View
- 10 Download
-
Related articles in
J Environ Anal Health Toxicol -
Removal of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Conventional Wastewater Treatment Plant2012 June;15(2)
Evaluation of Stability for Odorous Sulfur Compounds by Sampling Container2007 June;10(2)
Determination of Chlorphenols from the Indusrial Wastewater2005 March;8(1)