 |
 |
- Search
| J Environ Anal Health Toxicol > Volume 25(1); 2022 > Article |
|
ABSTRACT
The present study aimed to evaluate the concentration of odor substances and fine dust in areas where livestock farms are densely located, and to perform a correlation analysis of these concentrations to characterize the composition of fine dust. The mass concentration of fine dust in the areas tested was 33.6~46.68 μ/m3 for particulate matter with a diameter ≤ 10 μm (PM10) and 16.85~32.82 μ/m3 for particulate matter with a diameter ≤ 2.5 μm (PM2.5). These concentrations were higher than those in most of the neighboring areas. Ammonia concentration was measured in the range of 2.82~11.42 μ/m3. The concentrations of the volatile organic compounds (VOCs), methyl ethyl ketone and toluene, were 0.24~11.82 μ/m3, and 3.08~30.61 μ/m3, respectively. Composition analysis showed that fine dust was composed of 8.2~10.2% carbon, 0.3~1.7% sulfur, and 0.1~0.9% nitrogen. Anions were detected at a higher concentration than cations, and SO42- was measured at the highest concentration. Of the four most prevalent metals detected (i.e., Al, B, Cu, and Zn), Al showed the highest concentration in both PM10 and PM2.5, and accounted for the majority of the total metal component (84.7% and 82.2%, respectively). A correlation analysis of find dust with ammonia and VOC (methyl ethyl ketone and toluene) concentrations showed that ammonia generated from livestock facilities affected the formation of fine dust in nearby areas. VOCs emitted from nearby industrial facilities were also considered to contribute to the constituents of fine dust.
최근 미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5)에 대한 관심이 증가하면서 위해성 및 저감 대책에 대한 다양한 연구결과가 보고되고 있다. 미세먼지는 대기의 주요오염물질 중 하나이며, 기후, 가시성 및 인간 건강에 대한 악영향을 미치고 있다는 연구가 진행되고 있다[1]. 특히, 초미세먼지(PM2.5)는 2.5 μm 이하의 매우 작은 입자로, 폐포 깊숙이 침투하여 호흡기질환 및 심혈관계의 질환을 야기하는 등 인체 위해성이 높다는 연구가 보고되고 있다. 이러한 환경에 장기적으로 노출된 경우 조기 사망의 위험도가 증가한다고 알려져 있다[2]. 작은 크기의 물리적 특성에 따른 위해성뿐만 아니라, 미세먼지를 구성하고 있는 성분에 따라 그 위해성은 상이하다. 미세먼지는 화학적 성분의 복합혼합물로, 다양한 발생원에서 형성 및 배출되는 입자상 물질을 총칭하며 탄소성분(Carbonaceous Components), 미량금속(Trace Metal), 이온 성분(Ionic Components) 등 다양한 물질로 이루어져 있다[3]. 한편, 초미세먼지(PM2.5)는 자연적인 발생원보다는 인위적인 발생원에서 배출 및 생성되는 2차 오염물질이 많은 부분을 차지하고 있다. 특히, 황산화물(SOx), 질소산화물(NOx), 암모니아(NH3), 휘발성 유기화합물(VOCs) 등의 1차 오염물질과 전구물질이 존재하는 대기 중에서 광화학반응이 일어나고, 2차 오염물질인 황산염과 질산염이 형성되어 미세먼지의 발생빈도가 높아지고 있다[4]. Chen et al., (2014)[5]의 연구에 따르면 미세먼지(PM2.5)의 질량농도 중 약 38%가 수용성 화합물로 구성되어 있었고, 이 중 NO3-가 가장 풍부한 구성요소였으며 SO42-, NH4+로 구성되었다. Pathak et al., (2009)[6]의 연구에서는 미세먼지(PM2.5)의 구성성분 중 탄소 화합물, 특히 유기 탄소와 함께 수용성 무기 이온이 주요 부분을 차지했다고 보고 하였다. 미세먼지 구성성분 중 미량금속물질은 작은 부분을 차지하고 있지만, 비소, 카드뮴, 수은, 납과 같은 금속물질들은 비교적 발암성이 높고 효과적으로 분해되지 않는 물질이다. 미량금속물질의 중금속은 특히 장기간 노출되면 독성이 있는 것으로 밝혀졌다[7~9].
오늘날 삶의 질과 의식이 향상되어 환경문제에 관심이 증대되면서, 불쾌감을 주는 악취에 대한 민원이 점차 많아지고 있다. 국내 악취방지법에서는 두 가지 이상의 악취물질이 함께 작용하는 복합악취와 악취의 원인이 되는 물질의 지정악취로 구분하여 규제하고 있다. 이 중 지정악취는 황화합물류, 암모니아, 휘발성 유기화합물, 아민류, 알데하이드류로 구분하고 있다. 악취문제는 2003년 이후 축산시설에서 발생하는 악취로 인해 민원이 지속적으로 증가하고 있는 추세이다[10]. 특히, 축산시설에서 발생하는 악취 물질 중 암모니아와 황화합물 및 유기화합물은 가축분뇨 내에서 미생물이 유기물을 분해하면서 생성되는 대표적인 부산물로서[11] 미세먼지의 생성에 영향을 미치는 1차 오염물질과 2차 오염물질의 전구물질이다. 국내 축산시설 근무자의 호흡기질환인 천식(3.6%), 알레르기성 비염(29.2%) 발병률이 일반 지역보다 높다고 알려져 있으며, 이는 축산시설에서 발생하는 미세먼지의 경우 유기성물질이 포함되어 있기 때문으로 알려져 있다[12]. 농촌 지역은 도시지역보다 대기오염물질의 배출원이 적어 대기질이 양호할 것이라고 간주되고 있지만, 최근 경상남도 김해시 한림면은 축산시설이 밀집되어 있는 지역으로 악취문제에 대한 민원이 많은 지역 중 한 곳이다[13].
본 연구에서는 농촌 지역으로서 악취문제가 대두되고 있는 한림면의 9지점에서 2021년 01월부터 02월까지 악취유발물질(암모니아, 황화합물, 휘발성유기화합물)의 농도와 미세먼지의 질량농도를 측정비교하고, 악취유발물질의 농도에 따라 미세먼지를 구성하고 있는 화학적 특성을 분석하여 미세먼지의 형성 및 농도에 영향을 미치는 환경인자를 확인하고자 하였다.
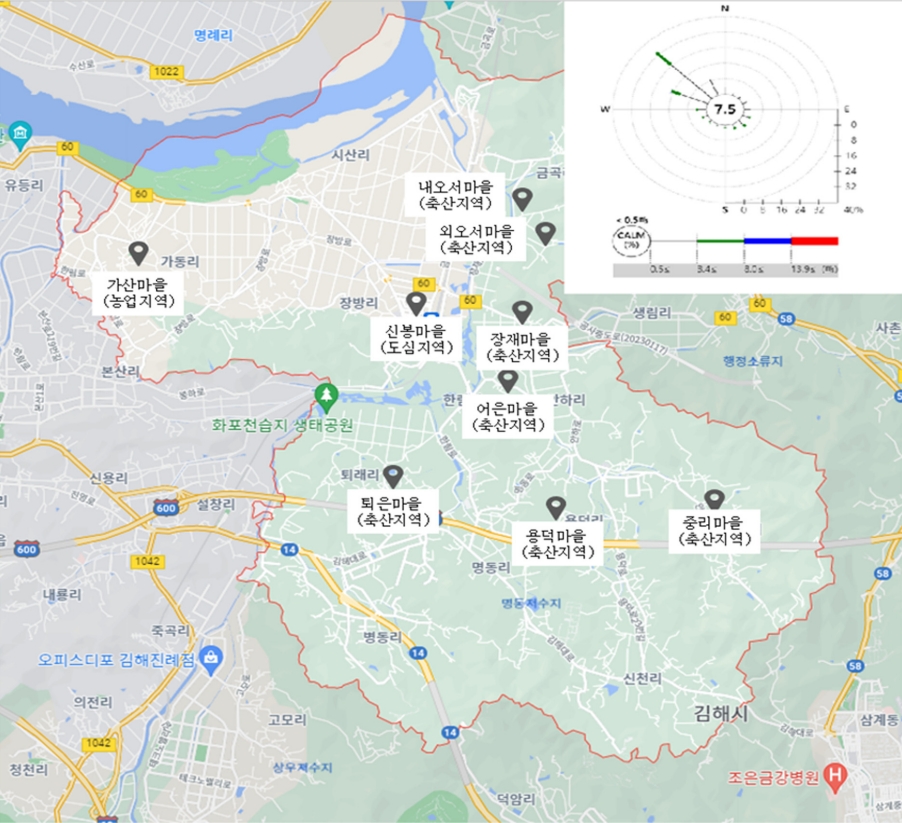
본 연구에서는 경상남도 김해시 지역 중 악취 민원이 빈번히 발생하고 있는 한림면의 마을회관 옥상을 시료 채취 위치로 선정하였다. 자료에 따르면 한림면은 김해시 19개 읍·면·동 중 가장 많은 축산시설이 모여 있는 지역으로서, 소의 경우, 시 전체 738개의 축산시설 중 343개(46%), 돼지는 105개 축산시설 중 61개 시설(58%)이 밀집된 지역이다. 2021년 01월부터 02월까지 가산리 마을회관 1곳, 금곡리 마을회관 2곳, 장방리 마을회관 1곳, 안하리 마을회관 2곳, 퇴래리 마을회관 1곳, 안곡리 마을회관 1곳, 용덕리 마을회관 1곳에서 총 9지점에서 3지점씩 5일간 미세먼지(PM10)시료 45개와 초미세먼지(PM2.5) 시료 45개의 시료를 채취하였다. 그리고, 악취농도의 정도를 파악하기 위해 지정악취인 황화합물류, 알데하이드류, 휘발성 유기화합물, 암모니아의 시료를 채취하여 측정·분석을 하였다. Table 1과 같이, 축산시설 인근 20 ~ 400 m 떨어진 지점, 도심지 인근, 그리고 농경지 인근의 마을회관 등을 포함하여 시료를 채취하였다.
시료 채취는 대기오염 공정시험기준(ES 01605.2, ES 01606.1)에 따라 실시하였다[14]. 시료 채취장치는 Low Volume Air Sampler(PMS-204, Korea)을 사용하였고, 16.7 L/min의 유량으로 24시간 포집하여 공기채취량을 약 24 m3가 되도록 채취하였다. 미세먼지(PM10)시료 채취는 여과지홀더 전단부에 10 μm 이상 제거할 수 있는 1차 분립장치를 설치하여 채취하였고, 초미세먼지(PM2.5) 시료 채취는 여과지홀더 전단부에 10 μm 이상 제거할 수 있는 1차 분립장치와 2.5 μm 이상 제거할 수 있는 2차 분립장치를 설치하여 실행하였다. 여과지는 47 mm Quartz Filter(WHATMAN 2.0 μm, United Kingdom)을 사용하였고, 채취 전 여과지에 함유된 불순물을 최소화하기 위해 전기 회화로에서 550oC, 24시간 전처리하여, 항온항습기에서 넣어 24시간 동안 항량시켜 보관하였다. 시료채취 전에 전자저울(ATX224, Japan)을 사용하여 여과지 질량농도를 측정하였고, 채취가 완료된 여과지는 4oC가 유지되는 시료 운반함을 사용하여 운반하고, 24시간 동안 항온항습기에 보관 후 질량농도를 측정하였고, 완료된 여과지는 4등분을 하여 미세먼지의 구성성분을 알아보기 위해 사용하였다. 1/4등분은 원소분석물질(C, N, S)을 분석하기 위해 사용되었고, 2/4등분은 4종의 음이온 성분(PO43-, Cl-, NO3-, SO42-), 4종의 양이온 성분(Ca2+, K+, Na+, Mg2+), 수용해성 유기 탄소(WSOC)를 분석하기 위해 사용하였고, 1/4등분은 19종의 금속류(Al, As, B, Ba, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ge, Li, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Se, U, V, Zn)를 분석하기 위해 사용하였다.
원소 물질분석은 열-광학 투과도법(Thermal-Optical Reflectance, TOR)을 이용한 원소성분분석기(2400 Series Ⅱ, Perkin Elmer, USA)를 사용하여 분석하였다.
음이온 성분은 보관된 여과지를 40 mL 바이알에 넣고 정제수 25 mL 주입한 후 초음파추출장치로 25oC로 1시간 동안 추출하여 0.22 μm Polypropylene Filter(PPF)로 여과하여 분석에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 미립자를 제거한 후 여과액을 분석하였다. 장비는 이온 크로마토그래프(CBM-20A, SHIMADZU, Japan)를 사용하였다. 용리액은 탄산수소나트륨(NaHCO3) 0.1676 g과 탄산나트륨(Na2CO3) 0.7412 g을 2 L 용량플라스크에 넣고 정제수로 녹여 표시 선까지 채워 사용하였고, IonPac AS14(4 mm × 250 mm) 컬럼에 1.2 mL/min의 유량으로 전기전도도검출기를 사용하여 분석하였다. 양이온 성분은 보관된 여과지를 40 mL 바이알에 넣고 정제수 25 mL 주입한 후 초음파추출장치로 25oC로 1시간 동안 추출하여 0.22 μm Polypropylene Filter(PPF)로 여과하여 분석에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 미립자를 제거한 후 여과액을 분석하였다. 장비는 유도결합플라즈마 발광광도기(ICP9820, SHIMADZU, Japan)를 사용하여 분석하였다.
수용해성 유기 탄소(WSOC)는 보관된 여과지를 40 mLᅠ바이알에 넣고 정제수 25 mL 주입한 후 초음파추출장치로 25oC로 1시간 동안 추출하여, 0.22 μm Polypropylene Filter(PPF)로 여과하여 분석에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 미립자를 제거한 후 여과액을 분석하였다. 장비는 총 유기 탄소 분석기(multi N/C 3100, analytikjena, Germany)를 사용하여 분석하였다. 시료에 포함된 무기 탄소를 10% 인 산으로 산성화시킨 후 이산화탄소로 산화시켜 제거하고 950oC의 고온에서 연소시킨다. 그리고 백금촉매로 산화시켜 이산화탄소로 전환시켜 발생한 이산화탄소는 NDIR (Non Dispersion Infrared Detector)로 검출하여 정량한다. 분석 시 사용한 표준용액은 프탈산 수소 칼륨으로 조제하여 검량곡선을 작성하였다.
지정악취 시료 채취는 악취공정시험기준(ES 09302.1a, ES 09303.1a, ES 09305.1a, ES 03907.a)에 따라 실시하였다[15]. 기상조건인 기온, 습도, 압력, 풍속을 비롯하여 지정악취물질로 분류되고 있는 암모니아, 황화합물류(황화수소), 알데하이드류(아세트알데하이드, 프로피온알데하이드, 뷰티르알데하이드), 휘발성유기화합물(톨루엔, 메틸에틸케톤)을 측정하였다. 채취시간은 오전 08:00에서 오전 10:00 사이에 실시하였고, 채취가 완료된 시료는 마개를 닫아 밀봉하여 4oC가 유지되는 시료 운반함을 사용하여 운반하고, 전처리 후 4oC에서 냉장보관하였다.
암모니아는 Mini Volume Air Sampler(JB-680B, Korea)의 시료 채취장치를 사용하였고, 연속된 2개의 흡수병을 직렬로 연결시켜 흡수액(0.5% 붕산 용액) 20 mL씩 넣고, 유량 10 L/min으로 5분간 시료를 채취하여 공기채취량을 약 50 L가 되도록 실시하였다. 흡수병은 흡수액 20 mL를 담을 수 있는 경질유리 재질의 여과 구가 있는 것을 사용하였다.
채취가 완료된 흡수액은 합하여 50 mL 용량플라스크에 옮기고 흡수액으로 표시 선까지 채운다. 이 용액 10 mL를 시험관에 옮기고 페놀-나이트로 프루시드 소듐 용액 5 mL, 하이포아염소산 소듐 용액 5 mL를 혼합하여 25oC ~ 30oC에서 1시간 방치한 후 640 nm 파장에서 흡광도를 이용하여 분석하였다. 장비는 자외선/가시선분광광 도기(SHIMADZU UV-1800, Japan)를 사용하여 분석하였다.
황화합물는 악취 포집 상자와 흡입 폄프(SARA-5100, Korea)의 시료 채취장치를 연결하여 사용하였다. 악취 포집 상자에 시료 주머니를 연결하고 유량 1 L/min으로 5분간 시료를 채취하여 공기채취량을 약 5 L가 되도록 실시하였다. 시료 주머니에 연결된 불소수지 재질인 흡입 마개를 열고, 흡입 펌프를 작동하여, 악취 포집기 내부를 감압하여, 시료 주머니에 시료를 채취하였다. 채취 전에 시료를 3회 이상 채우고 배기한 후 시료를 채취하였다. 시료 주머니는 폴리 비닐 플로라이드(PVF)재질의 테틀러백(Top-Trading, Korea)를 사용하였다. 채취가 완료된 시료 주머니는 전처리 없이 가스크로마토그래피 불꽃광도도검출기(SHIMADZU GC-2010 Plus, Japan)를 사용하여 분석하였다. 모세관 컬럼(60.0 m × 0.32 mm × 3.0 μm, Elite-1)을 사용하였고, 주입구온도(50oC), 검출기온도(290oC), 오븐 온도(50oC(5 min) ⟶ 10oC/min ⟶ 220oC(1min))로 분석하였다.
알데하이드는 Mini Volume Air Sampler(MP-Σ100H, Japan)의 시료 채취장치를 사용하였고, 폴리프로필렌(PP)튜브에 2,4-다이 나이트로 페닐하이드라진-실리카가 충전된 DNPH 카트리지(Top-Trading, Korea)를 사용하여, 유량 1 L/min으로 5분간 시료를 채취하여 공기채취량을 약 5 L가 되도록 실시하였다. 오존에 의한 방해를 제거하기 위해 내경 1.0 cm × 길이 4 cm의 폴리프로필렌(PP) 튜브에 아이오딘화포타슘(KI)결정을 채운 오존 스크러버를 DNPH 카트리지 전단에 연결하여 시료를 채취하였다. 채취가 완료된 2,4-DNPH 카트리지를 아세토나이트릴 용매로 추출하여 5 mL이 되도록 전처리하고, 고성능액체크로마토그래프(SHIMADZU LC-20AT, Japan)를 사용하여 분석하였다. 이동상으로 아세토나이트릴 용액과 정제수를 혼합하여 사용하였고, ACE5 C18역상(250 mm × 4.6 mm)컬럼에 1.0 mL/min의 유량으로 360 nm 파장의 자외선 검출기를 사용하여 분석하였다.
휘발성 유기화합물은 Mini Volume Air Sampler(MP-Σ30, Japan)의 시료 채취장치를 사용하였고, 소수성 흡착제가 충전된 Tenax Tube(KNR, Korea)를 사용하여, 유량 0.1 L/min으로 5분간 시료를 채취하여 공기채취량을 약 0.5 L가 되도록 실시하였다. Tenax Tube는 사용하기 전에 열 탈착 장치에 350oC에서 99.999% 질소기체 50mL/min으로 2시간 동안 안정화시킨 후 시료 채취를 하였다. 채취가 완료된 흡착관은 전처리 없이 가스크로마토그래피 질량분석기(SHIMADZU GCMS-QP2020 ULTRA, Japan)를 사용하여 분석하였다. 모세관 컬럼(60.0 m × 0.25 mm × 0.5 μm, DB-5)을 사용하였고, 주입구온도(50oC), 검출기온도(280oC), 오븐온도(60oC ⟶ 10oC/minᅠ⟶ 170oC ⟶ 20oC/min ⟶ 250oC(1 min))로 0.5 mL/minᅠ의 유속으로 50:1(Split ratio) 분할비로 분석을 하였다. 열 탈착기 250oC로 60 mL/min 유량으로 5 min 간 −20oC 에서 열 탈착을 실시한 뒤 가스크로마토그래피 질량분석기로 주입되었다.
본 연구의 신뢰성을 검증하기 위해 표준물질을 이용하여 검출한계, 정량한계, 정확도 및 정밀도,직선성을 측정하였다. 이온류의 검출한계(0.0005 μg/mL ~ 0.0133 μg), 정량한계(0.0015 μg/mL ~ 0.0423 μg/mL), 정확도(98.0% ~ 109.6%), 정밀도(0.1% ~ 4.36%)로 측정되었고, 결정계수(R2)는 0.99로 측정되었다. 중금속은 검출한계(0.0001 ~ 0.0009 μg/mL), 정량한계(0.0001 μg/mL ~ 0.0008 μg/mL),ᅠ정확도(85.0% ~ 111.0%), 정밀도(0.0% ~ 16.4%)로 측정되었고, 수용해성 유기탄소는 검출한계(0.0866 μg/mL), 정량한계(0.2758 μg/mL), 정확도(93.8%), 정밀도(1.5%)로 측정되었다. 결과적으로 검출한계, 정량한계, 정확도 및 정밀도,직선성은 적합한 수준에서 양호하게 측정하였다.
본 연구의 9개 측정지점과 바람 풍향 및 풍속을 기상청의 기상자료개방포털(https://data.kma.go.kr/cmmn/main)을 참고하여 Fig. 1에 나타냈다. 2021년 01월부터 2021년 03월까지 김해시(253)자료를 참고한 결과 한림면에서 북서풍 계열이 주 풍향이었으며, 풍속은 평균 7.5 m/s이였다. 이 데이터는 우리나라 겨울철 경상남도 및 부산에서 서북서 또는 북서풍 계열이 주 풍향이며 정형적인 겨울철의 풍향으로 관측되었다.
Table 2는 2021년 01월 31일부터 02월 25일까지 시료 채취 시 기상학적 지표변화(Weatheri(https://wwwweatheri.co.kr/index.php)에서 수집)를 나타내었다. 시료 채취 기간 동안 온도, 상대습도, 풍속, 기압은 각각 −3.8oC ~ 15.7oC, 22% ~ 86%, 1.3 m/s ~ 5.1 m/s, 754.30 mmHg ~ 768.90 mmHg 로 나타났다.
2021년 01월 31일부터 02월 04일까지 가산마을회관, 외오서마을회관, 내오서마을회관, 02월 14일부터 18일까지 신봉마을회관, 어은마을회관, 장재마을회관, 02월 21일부터 25일까지 퇴은마을회관, 장지마을회관, 용덕마을회관에서 채취한 PM10, PM2.5에 대한 질량농도는 Fig. 2에 나타내었다. PM10 농도는 최대 46.68 ㎍/m3(가산마을)에서 최소 33.61 μg/m3(신봉마을)로 측정되었다. 이는 환경기준인 24시간 평균농도(100 ㎍/m3)와 비교하면 33.6% ~ 46.7% 정도에 미치는 농도이다. 하지만, PM2.5 농도는 최대 32.82 μg/m3(용덕마을)에서 최소 16.85 μg/m3(장재마을)로 환경기준인 24시간 평균농도(35 μg/m3)와 비교하면 48.1% ~ 93.8% 정도로 나타났다. PM2.5/PM10의 비율은 최대 0.71(용덕마을)에서 최소 0.43(장재마을)으로 나타났고, 이는 용덕마을 미세먼지의 70% 이상이 PM2.5로 구성되어 있다는 것을 의미한다[16].
조사지역과의 미세먼지 농도를 비교하기 위해, (http://www.airkorea.or.kr)에서 수집된 인근 지역(경상남도 김해시 측정소(동상동, 삼방동, 장유동, 진영읍), 밀양시 측정소(내일동), 양산시 측정소(물금읍), 창원시 측정소(대산면))의 미세먼지 농도 정보를 확인하였다. 그 결과 김해시 진영읍의 경우를 제외하면 (PM10 농도가 조사지점들에 비해 대체로 높음), 대부분의 경우 PM10 및 PM2.5 농도는 9개 조사지점에서 높게 나타났다. 평소 축산시설의 악취문제가 심각한 김해시 한림면에서 미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5) 농도가 다른 주변 지역보다 높게 나타난 것은 악취유발물질이 미세먼지의 생성과 관련이 있을 수 있다는 것을 암시하고 있다.
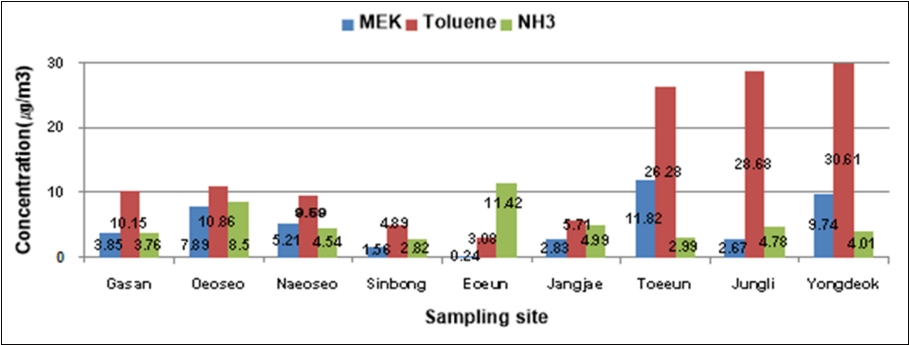
Fig. 3는 미세먼지를 채취하는 동안 악취물질 중 암모니아 및 VOCs 농도를 측정하여 나타냈다. 암모니아 평균농도는 도심지역인 신봉마을에서 최소(2.82 μg/m3)로 나타났고, 인근 축산시설이 있는 어은마을에서 최대(11.42 μg/m3)로 측정되었다. 어은마을은 측정지점 중에서 축산시설이 가장 근접한 지역으로서 높은 암모니아의 농도는 축산시설에서 기인하는 것으로 판단된다.
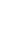
VOCs 중 메틸에틸케톤와 톨루엔의 평균농도는 인근 축산시설이 있는 어은마을에서 최소(0.24 μg/m3, 3.08 μg/m3)로 나타났고, 인근 축산시설이 있는 퇴은마을(11.82 μg/m3, 26.28 μg/m3)과 용덕마을(9.74 μg/m3, 30.61 μg/m3)에서 가장 높게 측정되었다. 이 두 지점은 인근에 축산시설이 근접해 있지만, 플라스틱 및 금속 가공·제조업과 같은 공업시설도 다수 존재하고 있으므로 배출가스의 영향을 받고 있는 것으로 판단된다.
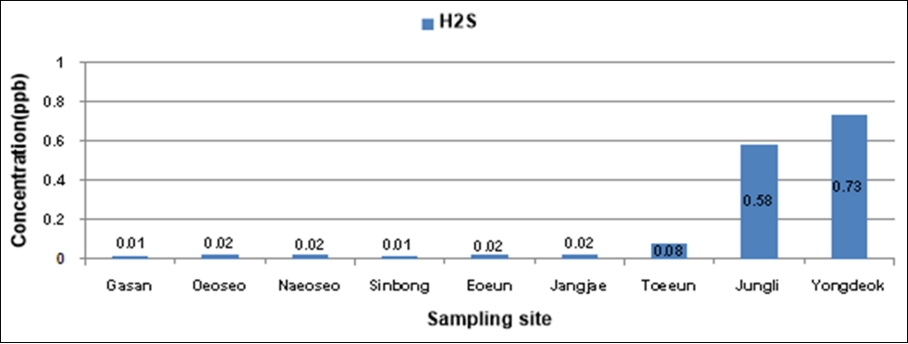
악취물질인 알데하이드류의 측정결과를 Fig. 5에 나타냈다. 폼알데하이드 농도는 농업지역인 가산마을에서 최소(5.1 μg/m3)로 나타났고, 도심지역인 신봉마을에서 최대(11.0 μg/m3)로 측정되었다. 아세트알데하이드 농도 역시 농업지역인 가산마을에서 최소(6.8 μg/m3)로 나타났고, 인근 축산시설이 있는 장지마을에서 최대(12.3 μg/m3)로ᅠ측정되었다. 프로피온알데하이드 농도는 인근 축산시설이 있는 용덕마을에서 최소(0.6 μg/m3)로 측정되었고, 도심지역인 신봉마을에서 최대(8.7 μg/m3)로 나타났다. 부틸알데히이드 평균농도는 인근 축산시설이 있는 외오서마을에서 최소(8.7 μg/m3)로 나타났고, 도심지역인 신봉마을에서 최대(28.512 μg/m3)로 측정되었다. Ye et al.(2006)[17]의 연구에 따르면 산업단지 및 주거지역에 대한 환경 대기 중 악취물질을 분석한 결과 카보닐 계열 성분 중에서는 아세트알데하이드가 가장 높게 나타났고, 폼알데하이드, 프로피온알데하이드 순으로 측정되었다. 도심지역인 신봉마을의 경우 겨울철 화석연료의 사용, 장지마을과 퇴은마을은 주변에 플라스틱 및 금속 가공 · 제조업과 같은 공업시설이 위치하고 있으므로 탄소성분의 알데히드류의 생성이 나타난 것으로 사료된다.
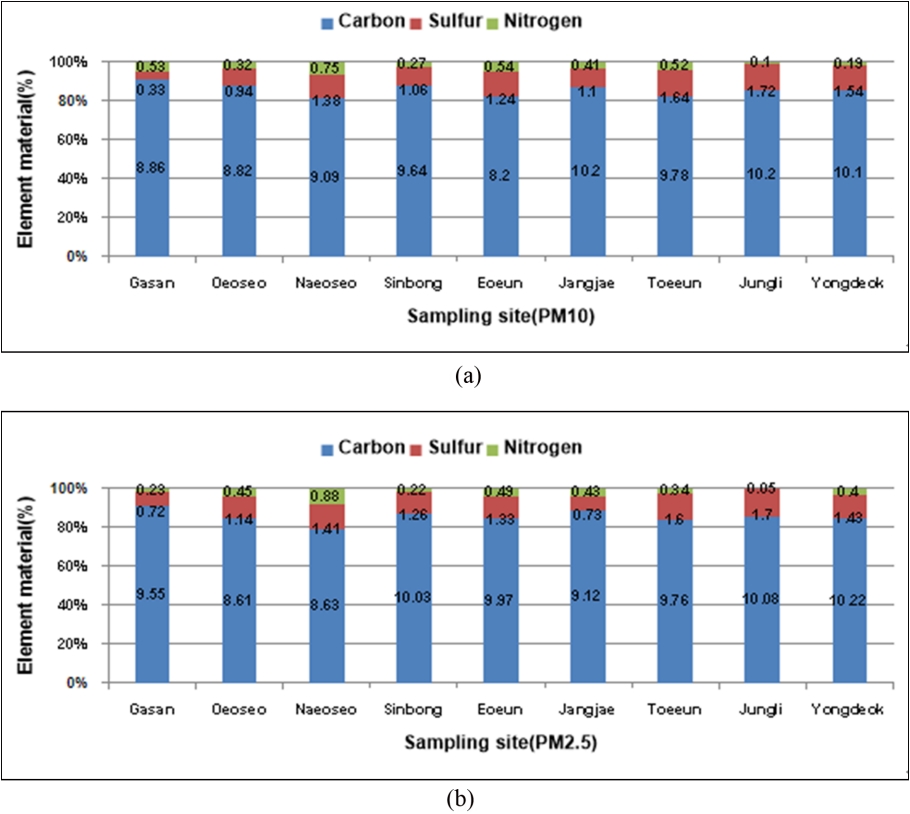
여과지에 채취된 미세먼지 3종의 탄소(C), 질소(N), 황(S) 구성 원소함유율과 수용해성 유기 탄소(WSOC)의 농도를 PM10(Fig. 6(a))와 PM2.5(Fig. 6(b))에 나타내었다. PM10에서 탄소(C)는 평균함유율 어은마을(8.2%) ~ 장재마을(10.2%), 황(S)이 평균함유율 가산마을(0.3%) ~ 중리마을(1.7%), 질소(N)가 평균함유율 중리마을(0.1%) ~ 내오서마을(0.8%)로 나타났고, PM2.5에서 탄소(C)는 평균함유율 외오서마을(8.6%) ~ 용덕마을(10.2%), 황(S)이 평균함유율 가산마을(0.7%) ~ 중리마을(1.7%), 질소(N)가 평균함유율 중리마을(N.D.) ~ 내오서마을(0.9%)로 나타났다. 그리고 WSOC 평균농도는 PM10 외오서마을(5.0 mg/m3) ~ 용덕마을(8.5 mg/m3)이 PM2.5 외오서마을(4.6 mg/m3)~ 용덕마을(8.6 mg/m3)보다 더 많은 농도가 함유되어 있었다.
미세먼지의 구성성분 중에 4종의 양이온(Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+)과 4종의 음이온(Cl-, NO3-, PO42-, SO42-)의 평균 질량농도의 측정결과와 상관관계를 계산하여 Table 3에 나타내었다. 그 결과 PM10과 PM2.5에서 각각 SO42-(2.82 μg/m3, 2.52 μg/m3)의 평균농도가 가장 높게 측정되었고, Cl-(1.59 μg/m3, 1.30 μg/m3), Na+(1.48 μg/m3, 1.10 μg/m3), NO3-(1.27 μg/m3, 1.06 μg/m3), K+(1.02 μg/m3, 0.98 μg/m3), Ca2+(0.93 μg/m3, 0.59 μg/m3), PO42-(0.16 μg/m3, 0.18 μg/m3), Mg2+(0.10 μg/m3, 0.06 μg/m3)순으로 나타났다. 이러한 결과는 Liu and Chung (2020)[16]에 연구에서 대전광역시의 미세먼지는 계절별 중 겨울철에 측정된 미세먼지 중에 있는 이온성분의 기여율이 높은 결과가 나타났고, 이온 성분 중 주로 구성하고 있는 물질은 NO3-와 SO42-인 것으로 나타났다. Jeoung et al., (2018)[20]의 연구에서는 논산시 농촌지역의 미세먼지를 측정하여 이온 성분을 분석한 결과 NO3-, SO42-가 높은 것으로 나타났다. Cl-와 Na+는 측정지점에서 약 10 km 떨어진 지점에 낙동강이 위치해 있어 해염입자(Sea Salt)의 영향을 받은 것으로 사료된다.
미세먼지의 구성성분 중에 19종의 금속류(Al, As, B, Ba, Cd, Co, Cu, Cr, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sb, Se, Sr, U, V, Zn)을 분석하여 그 결과를 Table 4에 나타내었다. 김해시 한림면 각 마을회관에서 측정한 PM10과 PM2.5를 구성하고 있는 금속류의 농도는 Al > B > Cu > Zn > Mn > Pb > Ba > Cr > Fe > Mo > V > Ni > Sr > As > Sb > Uᅠ> Se > Cd > Co의 순으로 나타났고, Al, B, Cu, Zn이 전체 금속류의 구성성분 중 각각 84.7%, 82.2%로 대부분을 차지하였다. 중금속은 지각 성분의 원소 중 Al, Fe등은 대체적으로 높게 나타났고, 비지각 성분의 원소인 Cd, Cr, Pb, Sr 등은 비교적 낮게 측정되었다. 이러한 결과는 Jeoung et al., (2018)[20]의 연구에서도 비슷한 결과를 보였다.
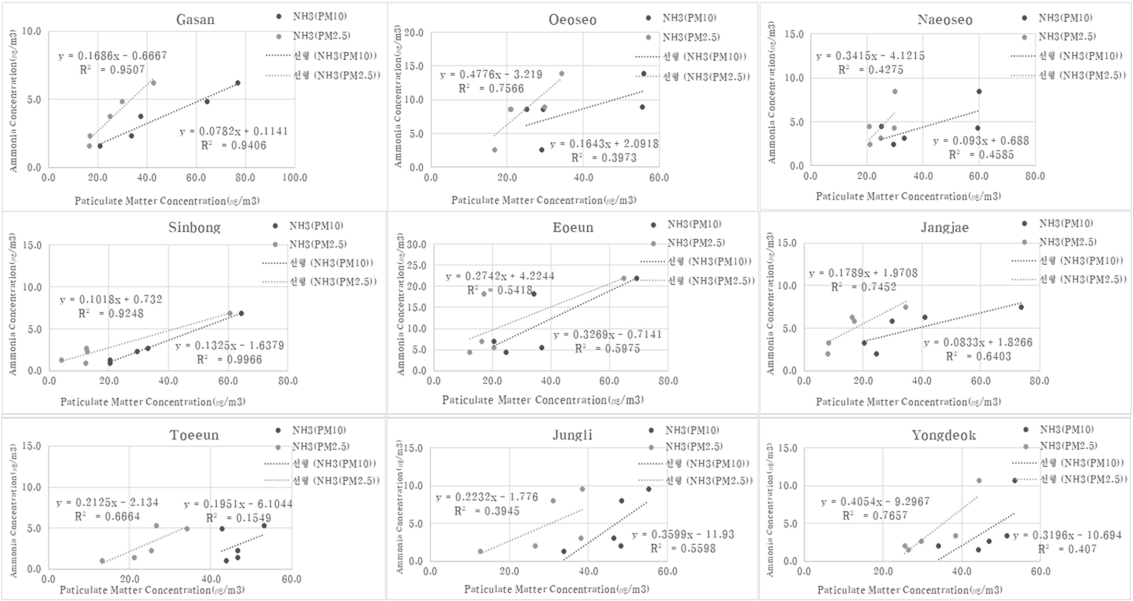
미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5) 질량농도와 암모니아 질량농도의 결정계수(R2)를 구하기 위해 가장 보편적으로 사용되고 있는 통계적인 기법으로 피어슨 상관분석법을 사용하여 Fig. 7에 나타냈다[18]. 9개의 모든 조사지점에서 미세먼지와 암모니아 간의 양의 상관도를 나타내었으며, PM10의 경우 4지점, PM2.5 의 경우 7지점에서 0.5 이상의 결정계수(R2)를 나타내었다. 특히, 농업지역(가산마을)에서 결정계수가 PM10(0.9406), PM2.5(0.9507), 도심지역(신봉마을)에서 PM10(0.9966), PM2.5(0.9248)로 가장 높은 연관성을 보였고, 유의 수준은 p < 0.01으로 나타났다. 인근에 축산시설이 가장 근거리에 있는 어은마을의 결정계수는 0.5975 (PM10) 및 0.5418 (PM2.5)로 악취물질(VOCs, 황화수소, 알데하이드류)보다 높은 연관성을 보였으며 이는 축산시설에서 배출되는 악취물질인 암모니아가 미세먼지의 생성에 어느정도의 역할을 하는 것으로 판단된다. 그 외 조사지역(8개)에서도 암모니아가 기타 악취물질 (e.g., VOCs, 황화수소, 알데하이드류)에 비해 상대적으로 높은 연관성을 나타내었다.
Fig. 8은 미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5) 농도와 VOCs(메틸에틸케톤, 톨루엔) 농도에 대한 상관도분석 및 결정계수(R2)를 나타내었다. 인근 축산시설이 있는 어은마을과 중리마을을 제외한 나머지 마을에서는 양의 관계를 나타났고, 이중에서 가산마을(도심지역)과 인근에 축산시설이 있는 퇴은 및 용덕마을에서 연관성이 높은 것으로 나타났다. 특히 도심지역(신봉마을)에서 메틸에틸케톤은 0.9169(PM10) 및 0.9723(PM2.5), 톨루엔은 0.9479(PM10) 및 0.9694(PM2.5)로 가장 높은 상관계수를 나타내었고, 유의 수준은 p<0.01으로 나타났다. 퇴은 및 용덕마을의 경우, 주변의 축산시설 이외에도, 인근 공업시설에서 배출되는 화학물질(e.g., VOCs)의 영향을 받고 있는 것으로 추정된다. 퇴은마을에서의 PM10 과 MEK 농도와의 높은 상관관계(결정계수 0.9899(MEK), 용덕마을의 PM10 및 PM2.5와 톨루엔과의 높은 상관관계(결정계수 0.7474 및 0.7162)가 이를 뒷받침하는 결과로 풀이된다. 한국환경정책·평가연구원의 보고서에 따르면[22], 미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5)는 자연적 발생보다는 인위적인 발생원에 의해 배출되어 생성되는 오염물질들이 많은 양을 차지하며, 특히 황산화물(SOx), 질소산화물(NOx), 암모니아(NH3), 휘발성유기화합물(VOCs)등의 전구물질들이 대기 중에 광화학 반응 등의 특정 조건에 의해 2차 생성이 되는데 이는 미세먼지와 휘발성유기화합물의 상관관계로서 설명을 뒷받침할 수 있다고 사료된다.
미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5) 질량농도와 황화수소의 질량농도에 대한 결정계수(R2)를 Fig. 9에 나타냈다. 도심지역(신봉마을)에서 0.8905 (PM10), 0.9914 (PM2.5)로 연관성이 높게 나타났고, p<0.01의 유의수준을 나타내었다. 퇴은마을에서는 황화수소의 기여도가 PM10보다 PM2.5가 높은 것으로 나타났다. 기타 지역에서는 유의미한 상관성이 확인되지 않았다. 도심지역인 신봉마을의 경우 겨울철 화석연료의 사용 및 퇴은마을의 경우 시료 채취 위치 주변에 플라스틱 및 금속 가공·제조업과 같은 공업시설이 위치하고 있어 대기 중에 배출된 황산화물(SOx)가 대기 중에 2차 반응에 의해 생성된 것으로 사료된다.
미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5)와 알데하이드류(폼알데하이드, 아세트알데하이드, 프로피온알데하이드, 부틸알데하이드)농도의 상관도 분석 및 결정계수(R2)를 Fig. 10에 나타냈다. 인근 축산시설이 있는 퇴은마을에서 PM10과 폼알데하이드와의 결정계수가 0.8056로 가장 높게 나타났고, 유의 수준은 p < 0.05으로 나타났다. 기타 아세트알데하이드, 프로피온알데하이드, 부틸알데하이드와 미세먼지 농도는 뚜렷한 연관성은 없는 것으로 나타났다.
Fig. 11은 미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5) 농도와 여과지에 채취된 원소성분(탄소, 황, 질소)에 대한 상관도분석 및 결정계수(R2)를 나타냈다. 탄소는 도심지역(신봉마을)에서 0.7646(PM10), 0.6323(PM2.5)로 높은 연관성을 보였고, 유의 수준은 p < 0.05으로 나타났다. 이는 앞에서 언급된 휘발성유기화합물(메틸에틸케톤, 톨루엔)들이 탄소성분의 구성요소로서 미세먼지 형성에 일부 기여하고 있는 것으로 판단된다. 질소는 농업지역(가산마을)에서 0.7101(PM10), 0.9525(PM2.5), 도심지역(신봉마을)에서 0.9419(PM10), 0.8907 (PM2.5), 인근 축산시설이 가장 근거리에 있는 어은마을에서 0.9255(PM10), 0.9929(PM2.5)로 연관성이 높은 것으로 나타났으며, 유의기준은 p < 0.05으로 나타났다. 이 또한 축산시설 등으로부터 발생된 암모니아가 미세먼지 형성에 영향을 미친 것으로 판단된다.
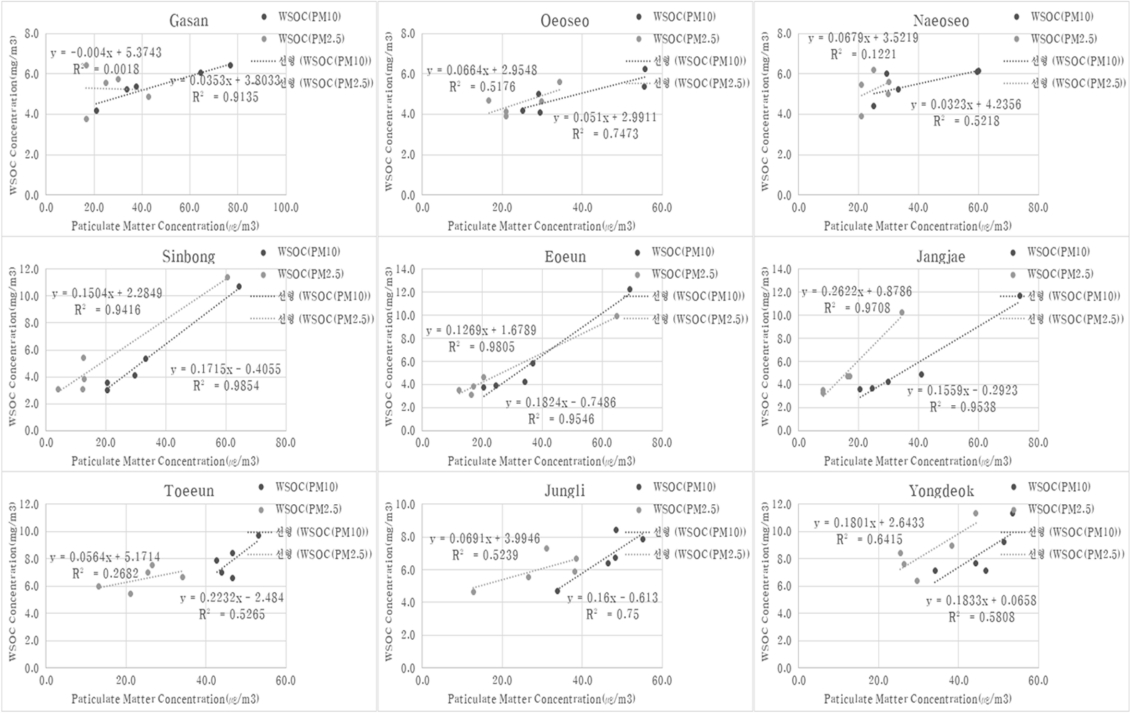
Fig. 12은 미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5) 질량농도와 여과지에 채취된 WSOC 질량농도에 대한 결정계수(R2)를 나타냈다. 도심지역(신봉마을)이 0.9854(PM10), 0.9416(PM2.5), 인근 축산시설이 있는 어은마을이 0.9546(PM10), 0.9805(PM2.5), 장재마을이 0.9538(PM10), 0.9708(PM2.5)로 WSOC 농도와 높은 연관성이 있는 것으로 나타났고, 유의 수준은 모두 p < 0.01으로 나타났다.
미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5) 농도와 여과지에 채취된 8종의 이온류(Na+, Mg2+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-, NO3-, PO42-, SO42-)농도에 대한 상관도분석 및 결정계수(R2)를 Fig. 13에 나타냈다. 8종의 이온류 중 양이온보다 음이온이 연관성이 더 있는 것으로 나타났고, 특히, NO3-, SO42-가 가장 높은 연관성을 나타냈다. NO3-는 농업지역(가산마을)에서 0.8818(PM10), 0.9539(PM2.5), 도심지역(신봉마을)에서 0.9684(PM10), 0.9665(PM2.5), 인근 축산시설이 있는 어은마을에서 0.9282(PM10), 0.9994(PM2.5)로 가장 높은 연관성을 보였고, 유의 수준은 p < 0.01으로 나타났다. 또한, SO42-는 도심지역(신봉마을)에서 0.9524(PM10), 0.9631 (PM2.5), 인근 축산시설이 있는 어은마을에서 0.9728 (PM10), ᅠ0.9717(PM2.5)로 가장 높은 연관성을 보였고, 유의 수준은 p<0.01으로 나타났다. 이는 질산염과 황산염이 미세먼지를 구성하는 직접적인 원인물질로 작용하고 있다는 것을 암시한다[19]. Jeong et al.,(2018)[20].)의 연구에서는 NH4+과 NO3-(0.89), NH4+과 SO42-(0.88)이 매우 높은 상관성을 가지고 있다는 것을 확인하였다. 따라서, 악취물질 중 하나인 암모니아가 미세먼지의 형성에 관련이 있을 것으로 판단된다.
Fig. 14는 농업지역(가산마을), 도심지역(신봉마을), 그리고 축산시설이 인근에 위치한 7개 지역(외오서마을, 내오서마을, 어은마을, 장재마을, 퇴은마을, 중리마을, 용덕마을)에서 미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5)와 암모니아의 연관성을 나타냈다. PM10과 암모니아는 농업지역(가산마을)보다 도심지역(신봉마을)과 인근 축산시설지역에서 높게 나타났다. PM2.5와 암모니아는 축산시설밀집지역이 농업지역(가산마을)과 도심지역(신봉마을)보다 높은 상관관계를 나타내었다. 이는 인근 축산시설지역에서 배출되는 암모니아가 PM10보다는 PM2.5에 미치는 영향이 상대적으로 더 큰것으로 판단된다. Kang et al., (2004)[21]에 연구에 따르면 2001년 10월부터 11월까지 서울특별시의 미세먼지 구성 성분 중 이온농도를 측정한 결과 PM2.5의 평균질량농도에 크게 기여한 이온물질은 NH4+, NO3-, SO42-을 확인하였고, Liu and Chung (2020)[16]에 연구에서는 대전광역시 2018년 07월부터 2019년 05월까지 계절에 따라 미세먼지를 측정하여 이온의 구성성분을 분석한 결과 여름철에는 SO42-가 가장 높게 나타났고, 겨울철과 황사기간에는 NH4+가 가장 높은 결과를 확인하였다. 이는 악취유발물질 중 암모니아가 미세먼지와 높은 상관관계가 있는 사실을 뒷받침한다.
악취 민원이 빈번히 발생하고 있는 경상남도 김해시 한림면에서 미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5) 시료를 측정하여 질량농도와 그에 따른 구성성분을 분석하였고, 악취유발물질과의 연관성을 알아보기 위해 상관도분석을 수행하였다. 한림면 마을에서 PM10 평균 질량농도는 최소 33.61 μg/m3에서 최대 46.68 μg/m3로 측정되었고, PM2.5 평균 질량농도는 최소 16.85 μg/m3에서 최대 32.82 μg/m3로 측정되었으며, 인근의 축산시설이 있는 한림면의 마을이 인근 주변의 지역보다 대부분 높게 나타났다. 미세먼지와 악취물질 중 암모니아, VOCs(메틸에틸케톤, 톨루엔)와 연관성을 분석한 결과 미세먼지(PM10, PM2.5)와 암모니아의 상관관계가 9개의 모든 조사지점에서 높은 연관성이 있는것으로 나타났다. 도시지역에서는 VOCs(메틸에틸케톤, 톨루엔)와의 상관관계도 높게 나타났는데 이는 주변 플라스틱 및 금속 가공·제조업과 같은 공업시설에서 유해한 배출오염물질의 영향을 받는 것을 판단된다. 한편, 축산시설이 가장 인근에 위치한 어은마을에서는 미세먼지와 암모니아는 높은 상관관계를 보여주었으나, 휘발성 유기화합물과는 낮은 상관성을 나타내었다. 이는 축산시설에서 배출되는 암모니아가 미세먼지의 형성에 보다 많은 영향을 미치는 것으로 판단된다. 퇴은마을과 용덕마을도 인근에 축산시설이 있어 암모니아의 연관성이 있는 것으로 나타났지만, 주변의 플라스틱 및 금속 가공·제조업과 같은 공업시설에서 배출되는 휘발성 유기화합물 등이 미세먼지 생성에 영향을 미치는 것으로 사료된다. 해당 연구결과는 암모니아, 황화합물, 휘발성유기화합물 등의 악취유발물질이 미세먼지의 형성과정에 어떻게 관여하고 있는지를 규명하는데 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
Fig. 8.
Results of coefficient of determination VOCs((a)Methylethylketone, (b)Toluene) for PM10 and PM2.5.
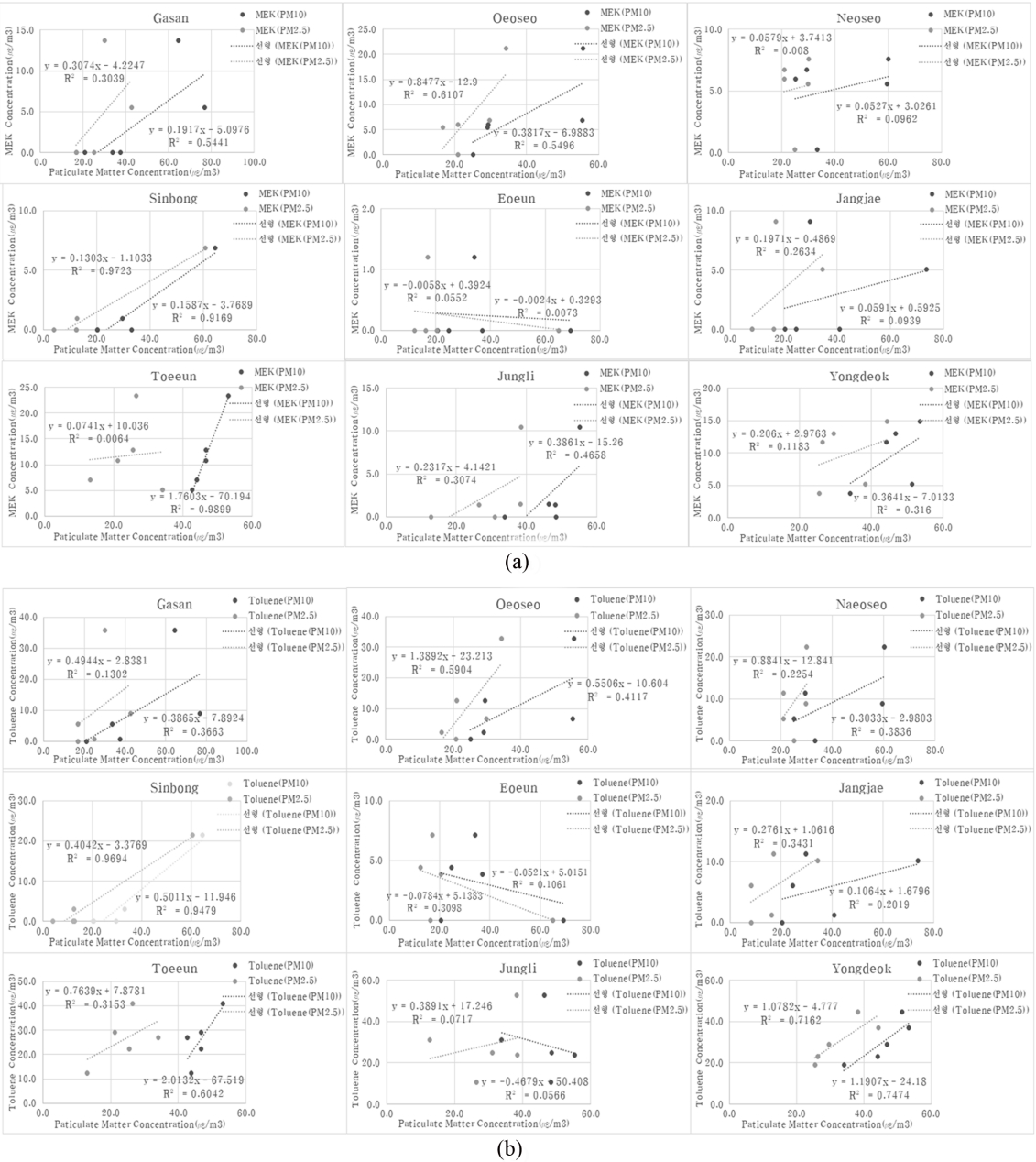
Fig. 11.
Results of coefficient of determination element material((a) carbon, (b) hydrogen) for PM10 and PM2.5.
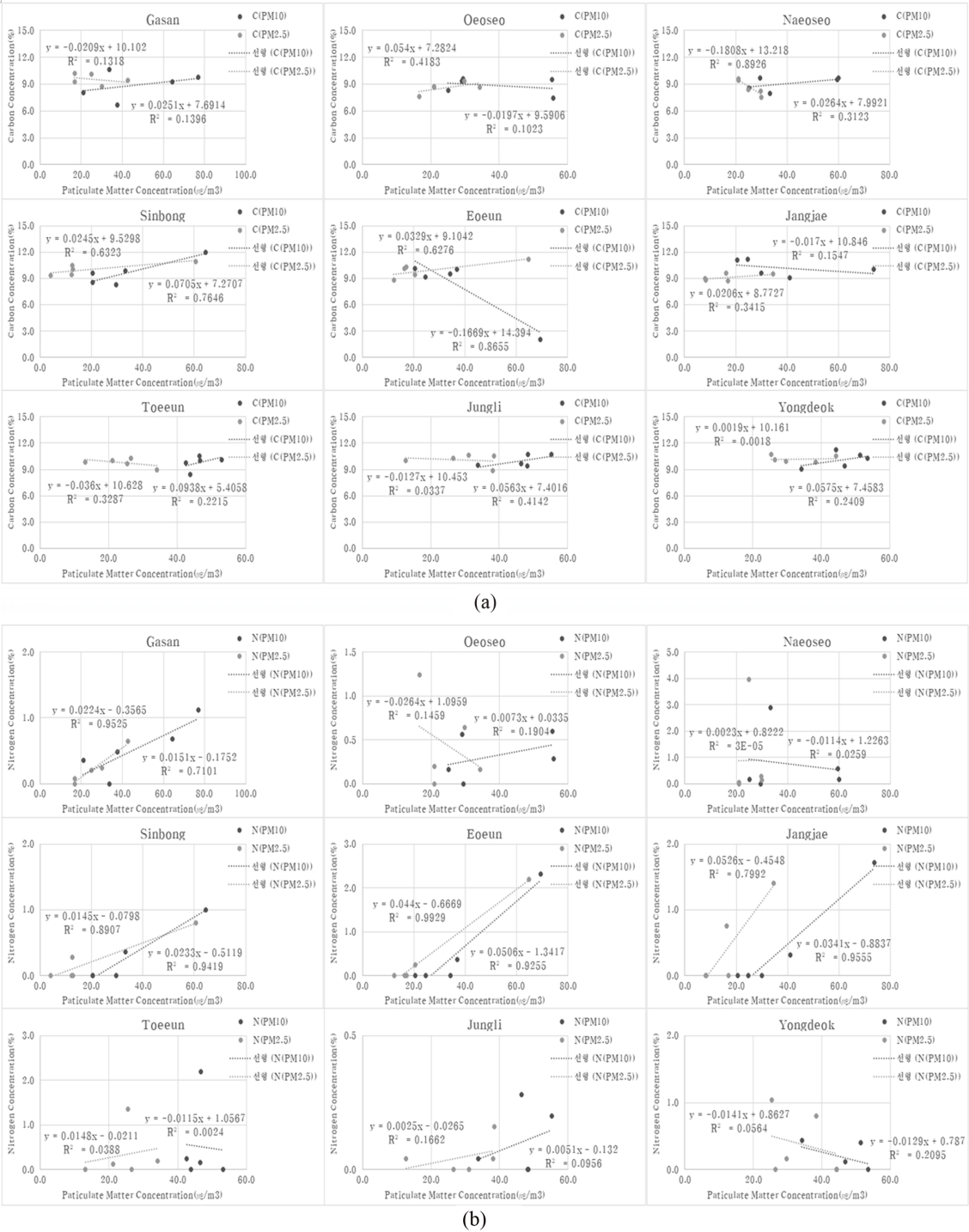
Fig. 14.
Results of coefficient of particulate matter(PM10, PM2.5) and Ammonia for agricultural area, urban area and livestock areas.
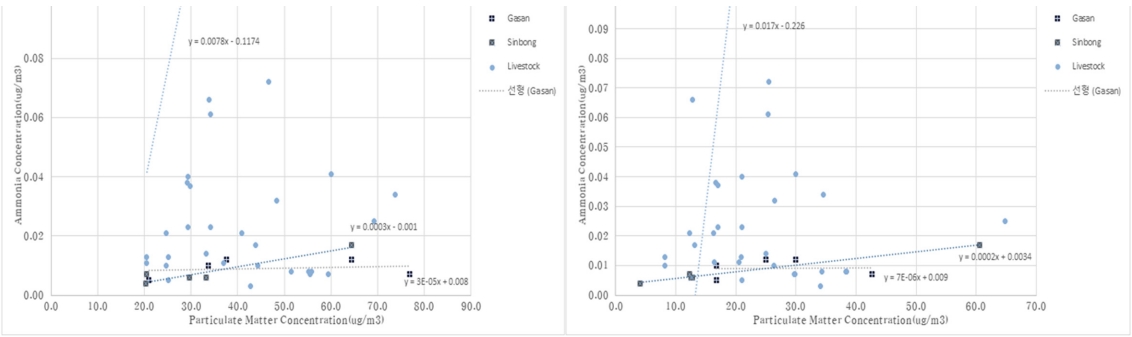
Table 1.
Location and description of sampling sites in Hallim-myeon, Gimhae, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea
Table 2.
Statistics of temperature, relative humidity, wind speed and atmospheric pressure in study area (i.e. Hallim-myeon, Gimhae, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea)
Table 3.
Concentration of ions within the PM10 and PM2.5 (unit : μg/m3)
Table 4.
Concentration of determination of metals at the PM10 and PM2.5 (unit : μg/m3)
참고문헌
1. M. J. Nieuwenhuijsen, P. Dadvand, J. Grellier, D. Martinez, and M. Vrijheid, “Environmental risk factors of pregnancy outcomes: a summary of recent meta-analyses of epidemiological studies”, Environ. Health, 2013, 12 (1), 1-10.


2. W. Zhou, D. Tian, J. He, L. Zhang, X. Tang, L. Zhang, Y. Wang, L. Li, J. Zhao, X. Yuan, and S. Peng, “Exposure scenario : Another important factor determining the toxic effects of PM2.5 and possible mechanisms involved”, Environmental Pollution, 2017, 226, 412-425.


3. J.-K. Choi, J.-B. Heo, S.-J. Ban, S.-M. Yi, and K.-D. Zoh, “Chemical characteristics of PM2.5 aerosol in Incheon, Korea”, Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 60, 583-592.

4. S. S. Park, and S. Y. Cho, “Tracking sources and behaviors of water-soluble organic carbon in fine particulate matter measured at an urban site in Korea”, Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45 (1), 60-72.

5. J. Chen, S. Qiu, J. Shang, O. M. F. Wilfrid, X. Liu, H. Tian, and J. Boman, “Impact of relative humidity and water soluble constituents of PM2.5 on visibility impairment in Beijing, China”, Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 2014, 14 (1), 260-268.

6. R. K. Pathak, W. S. Wu, and T. Wang, “Summertime PM2.5 Ionic Species in four Major Cities of China : Nitrate Formation in an Ammonia-deficient Atmosphere”, Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2009, 9, 1711-1722.

7. N. A. Greene, and V. R. Morris, “Assessment of Public Health Risks Associated with Atmospheric Exposure to PM2.5 in Washington, DC, USA”, Environmental Research and Public Health, 2006, 3 (1), 86-97.



8. X. Liu, J. Zhu, P. V. Espen, F. Adams, R. Xiao, S. Dong, and Y. Li, “Single particle characterization of spring and summer aerosols in Beijing : Formation of composite sulfate of calcium and potassium”, Atmospheric Environment, 2005, 39 (36), 6909-6918.

9. Y. Gao, and H. Ji, “Microscopic morphology and seasonal variation of health effect arising from heavy metals in PM2.5 and PM10 : One-year measurement in a densely populated area of urban Beijing”, Atmospheric Research, 2008, 212, 213-226.

10. 은영 이, and 소진 이, “돈분뇨로부터 발생하는 암모니아의 배출 특성”, 한국미생물생명공학회지, 2010, 38 (3), 308-314.
11. 기연 김, 홍림 최, 한종 고, and 치년 김, “축분 퇴비화 과정 중 퇴비 부숙도를 고려한 암모니아 발생량 산정”, 한국축 산학회지, 2006, 48 (1), 123-130.
12. 경석 권, “축산분야 미세먼지 연구 동향 : 축산 미세먼지 로 인한 영향과 발생 특성”, 한국농공학회지, 2020, 62 (2), 15-23.
13. 성욱 정, 기영 변, and 흥재 박, “김해시 본산공단 주변지역의 환경대기 중 주요 악취물질의 농도 특성에 관한 연구”, 한국환경과학회지, 2012, 21, 49-55.
14. 국립환경과학원, "대기오염공정시험기준", 2020, 제 2020-30호
15. 국립환경과학원, "악취공정시험기준", 2019, 제2019-17호
16. 내녕 유, and 진도 정, “계절별 대전시 미세먼지 중 이온성분 특성에 관한 연구 -고용량볼륨에어샘플러 이용하여-”, 한국환경기술학회지, 2020, 21, 131-137.
17. 여진 최, 기현 김, and 의찬 전, “산업단지 및 주거지역에 대한 환경대기 중 주요 악취물질의 농도특성에 관한 연구 - 안산시 반월공단을 중심으로-”, 한국지구과학회지, 2006, 27, 209-220.
18. 정훈 엄, 세영 박, 승미 권, 진호 신, 석주 조, and 현욱 김, “디누더(Denuder)장착 여부에 따른 초미세먼지(PM2.5) 중 암모늄 과대평가와 이온밸런스에 관한 연구”, 한국환경 분석학회지, 2021, 24, 100-106.
19. 지용 김, 솔 허, 승근 이, and 병로 유, “통계분석을 이용한 대 전지역 미세먼지(PM10)의 중금속 및 이온 성분 특성 연구”, 한국환경기술학회지, 2020, 21, 64-71.
20. 진희 정, 종명 임, and 진홍 이, “농촌지역 대기 중 PM2.5의 화학적 특성과 오염원 정량 평가”, 한국환경영향평가학회지, 2018, 27, 431-446.
21. C.-M. Kang, H. S. Lee, B.-W. Kang, S.-K. Lee, and Y. Sunwoo, “Chemical characteristics of acidic gas pollutants and PM2.5 species during hazy episodes in Seoul, South Korea”, Atmospheric Environment, 2004, 38 (28), 4749-4760.

22. 배현주, 이승민, 정다운, 오규림, 김시진, 이종태, "인체 위해 저감방안 마련을 위한 미세먼지 구성성분별 건강 영향연구", 2020, 환경포럼, 240, 1-19